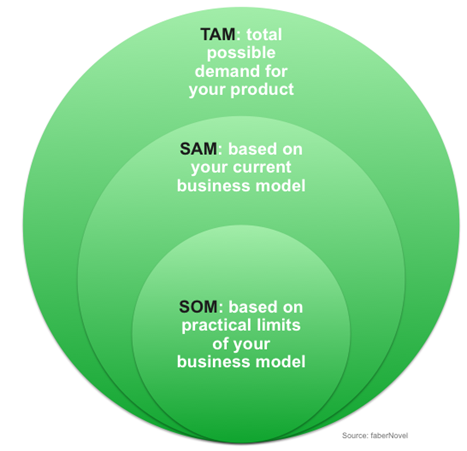
Sizing the Customer Market
•TAM or Total Available Market is the total market demand for a product or service.
•SAM or Serviceable Available Market is the segment of the TAM targeted by your products and services which is within your geographical reach.
•SOM – Serviceable Obtainable Market or Share of Market is the portion of SAM that you can capture.
Market Research Sources
Industry Canada for info on companies
Strategis – www.strategis.ic.gc.ca
Financial Performance Data – www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/pp-pp.nsf/eng/home
Keyword searching – The key to research
By default “Plural” is automatic when searching keywords
•However Apple and Apples yield different search results
The wildcard *
•Educat* searches for educate, educated, educator, etc.
•The question mark (?) searches for variants
•searching for colo?r would return both color and colour.
MaRS Discovery District
Educators, researchers, social scientists, entrepreneurs and business experts under one roof
Your business must align with the key sectors: cleantech; fintech; health; enterprise (high growth with tech solutions)
Market Intelligence: Research reports; Expert analysis
Market Intelligence Databases https://www.marsdd.com/market-intelligence/
Access to Market Intelligence via Anne Dorsey
Customer Discovery & Development Purchasing Decisions & Pricing
Customer Discovery:
In fact, customer discovery ordinarily involves a process that closely follows the traditional scientific method:
1. Observing and defining a phenomenon (problem or market need)
2. Developing a hypothesis about a solution to the problem (business idea)
3. Conducting an experiment to test the hypothesis (getting “out of the building”)
Step One: Define a Hypothesis
The first step is to form a hypothesis that defines both the problem and the solution you are proposing. A simple way to frame this is to fill in the following sentence:
My idea solves [insert problem] by [insert solution].
Step Two: Define Your Assumptions
In detailing your hypothesis, you will be forced to make some assumptions about your idea. These will include assumptions that:
• The problem you addressed is actually a problem
• The solution you propose will actually solve the problem
• The market you plan to target has this problem
• The market you plan to target will be willing to pay for your solution
Step Three: Ask (Good) Questions
The next step is to “get out of the building” and ask some
questions.
•Start by targeting people who you believe could be potential customers.
•If you’re running a college tutoring business, you should not be asking your parents questions. They are not going to be your customers.
•Ask the people that you anticipate asking to buy your product
in the future. They hold the answers.
Next, you’re going to ask “detective” questions.
•This isn’t just “asking around” for people’s thoughts on your idea, though.
•In fact, you really shouldn’t mention your idea at all. This is because customer discovery allows you to let your customers build your product for you. Discovery questions are open-ended and nonspecific about your idea. By letting the customer lead the conversation, you will end up letting them tell you about their ideal solution (instead of the other way around).
Discovery Interview Do’s & Don’ts
•Don’t push with your opinion or solution
•No leading questions
•Be an information gatherer, not a problem solver
•Do ask open ended questions
•Be open minded and listen
•Exploit opportunities to learn
•Seek customer learnings / experiences (stories)
•Ideally face to face or phone/skype
•Have a second observer to make notes if possible
•Allow the customer to tell you their exact opinions (or lack of opinion) about your topic of interest.
•If they feel extremely strongly about the problem, you’ll see pretty quickly by their body language and tone of voice.
•If they don’t see much of a problem, they may seem confused or complacent.
•They might identify a different problem than you imagined.
•As you get more responses from potential customers, your product will start to make more sense or less sense.
Step Four: Evaluate and Refine
•Chances are you’ll discover some things that you had not originally considered.
•You have the opportunity to return to (Step One), incorporate what you’ve learned, and repeat the process.
•Once your customers’ responses match your hypothesis, then you can build something that your customers will actually want.
•Don’t build the fastest product, building the best product.
Three common challenges when it comes to customer discovery:
entrepreneurs worry about their idea being stolen
entrepreneurs spend too much time explaining/pitching their idea rather than listening
entrepreneurs are uncomfortable approaching strangers, and fear rejection
Problem-solution fit
Customer Discovery: 4 Steps
Step One: Define a Hypothesis
Step Two: Define Your Assumptions
Step Three: Ask (Good) Questions
Step Four: Evaluate and Refine
Customer Development Process
Customer discovery is when the founder’s vision is captured and turned into a series of business model hypotheses. This is then developed into a plan to test the customer reactions and collect their responses as usable data.
Customer validation tests come next to see if the resulting business model is repeatable and scalable. If it is not, then it means returning to the customer discovery of step one.
Customer creation is the start of execution and builds end-user demand. It also drives that demand into the sales channel to scale the business.
Transition (or Company Building)… the company from a startup to an organization that is focused on executing a validated model.
Customer Validation ….. you have a product that customers need and has been validated in the real world with some paid users. Customer validation is validating the sales and marketing roadmap that will help you gain more market share and customers.
Ideation, Rapid Prototyping & Startup Teams
What are the principles of an elegant solution?
It is self-explanatory.
It solves more problems than it creates.
Ingenuity. Considers the problem from a unique angle and arrives at a simple solution.
How does your solution solve the pain?
It has to provide WIIFM (What’s in it for me…the customer?)
What value does your solution deliver?
-Time savings
– Money saving or money making
– Convenience
– “Cool” Factor
– Environmental benefits
– Aesthetics
– etc…
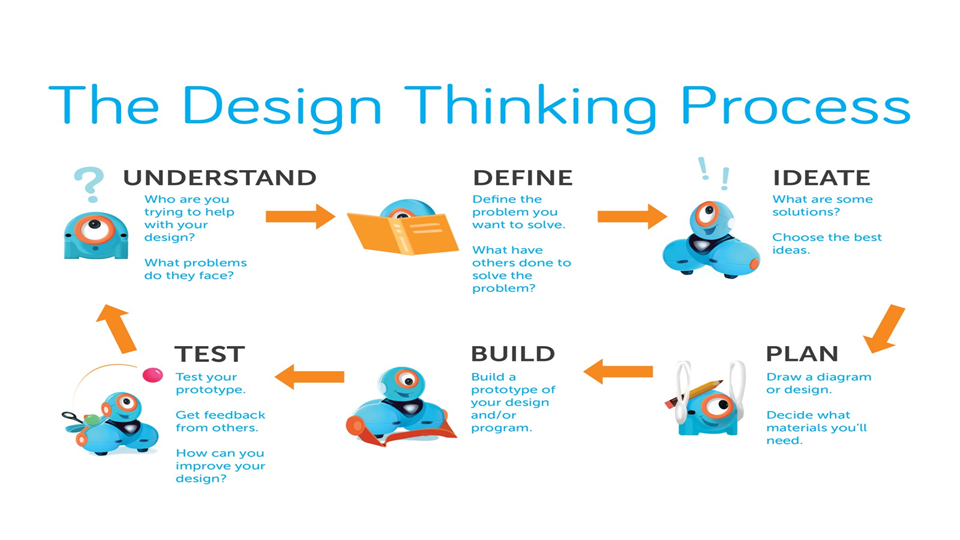
To ideate:
-Get your team together
-Clearly identify the problem
-No judging rule
-Group brainstorm session
-Whiteboard the ideas
-Sort them…categories
-Evaluate…do they solve the problem?
-Blue sky discussion on the exciting solutions
-Is there an elegant solution?
What is rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is the process of quickly mocking up the future of an idea, product or service….. be it a drawing, a website, an app, or a physical device.
……. Then validating it with a broader team of users, designers, or stakeholders
could be a visual or physical demonstration
Startup for Everyone Definition:
You need a product person, a sales/operations person, and a design/marketing person.

Watch outs….
Think twice about working with friends and family
•Often they think like you do
•Hard to terminate (fire) friends and family
•Do they have complimentary skill sets?
•Business and social relationships can conflict
•Breakups happen. Can be permanent
Protecting Intellectual Property: business is business, your friend may destroy your IP.
IP: creations of creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce. IP is a valuable business asset. IP can be sold, licensed or traded.
Benefits of IP information: avoid duplication of effort, prevent infringement, keep competitors from your market, get money from license.
Common forms of IP: Trade secrets, Patents, Trade-marks, Copyrights, Industrial designs
Trade secret: business confidential information. KFC secret recipe.
Patentable: product, composition or formula, machine, process or its improvement. Invention must be new, useful, inventive.
Patenting process: prior to filing an application (CIPO) , Applying must be done before public disclosure.
Searching Patent: Prior art, Infringement


What is copyright: It is the exclusive right to produce or reproduce a creation. Literary, Dramatic, Musical, Artistic. You own it when you create it. But you should register it to prove that you created it.
•Copyright is automatic upon creation and registration provides a legal advantage
– Only form of protection that is world-wide
•Use proper marking: © owner’s name, year
•Term is generally life of creator plus 50 years
Industrial designs must be registered for protection
–Keep confidential prior to filing
–Search, file with Canadian Intellectual Property Office and await a response
–Provides the owner with the exclusive right to make, use and sell the design
•Design registration up to 15 years of protection in Canada. (10-25 in some countries)
RELATED POSTS
View all




